P&K 3783 (VDI 3783 part 1+2)
Dispersion areas types I-XXV
Dispersion areas
Index
Dispersion area types I to V
Area maps for types I to V
Dispersion area types VI to IX
Area maps for types VI to IX
Dispersion area types X to XVIII
Dispersion area types X to XII
Area maps for types X to XII
Dispersion area types XIII to XV
Area maps for types XIII to XV
Dispersion area types XVI to XVIII
Area maps for types XVI to XVIII
Dispersion area types XIX to XXI
Area maps for types XIX to XXII
Area maps for types XXIII to XXV
Table of input data for instantaneous release
Table of input data for continuous release
Dispersion area types I to V
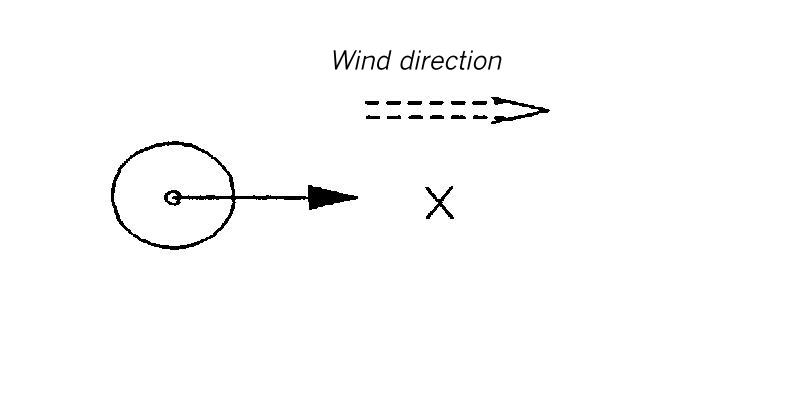
Dispersion area type I
This type of dispersion area can be used for accidental releases in flat terrain without obstacles. Furthermore, it can replace all the dispersion areas with obstacles which lead to a reduction of the concentration if no special diagrams are available.
Dispersion area type II
This type of dispersion area can be used for accidental releases in which the dispersion is limited by an obstacle to a hemisphere. The obstacle can consist of a row of buildings, a dam, a dock or similar objects near the source. This type of dispersion area may also be used for shorter obstacles or other heights at larger distances, if no other special diagrams are available. If the distance of the obstacle amounts to more than 5 Lei (for instantaneous release) or 30 Lee (for continuous release), the effect of the obstacle on the heavy gas dispersion can be disregarded.
Dispersion area type III
This type of dispersion area can be used for accidental releases for which the dispersion is limited by an uninterrupted canyon of orthogonal walls which is parallel to the wind. This type of dispersion area can also be used for canyons of other geometries if no other special diagrams are available therefore. Deeper canyons lead to similar concentrations. For lower, broader or interrupted canyons, it will yield conservative estimations. For single, interrupted buildings, the (*UZD) lower flammability distances are considerably overestimated if the diagram of dispersion area type III is used.
Dispersion area type IV
For this type of dispersion area, a hemispherical, impermeable protective wall is located at such a distance leeward of the source that a distinct protection is obtained for those locations which are situated beyond the wall. On the bases of the results, the potential protection effect of such a measure can be estimated.
Dispersion area type V
In contrast to dispersion area type IV, the protective wall is placed nearer to the source for this type of dispersion area, and the protecting effect decreases.
Area maps for types I to V
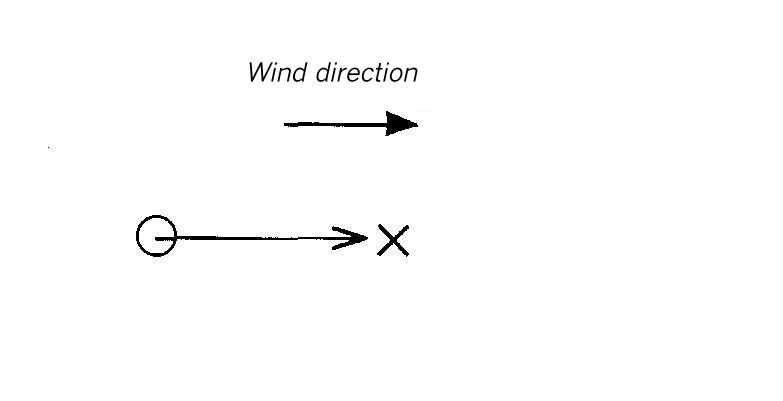
Area map for dispersion area type I
Flat terrain without obstacles.
Area map for dispersion area type II
Flat terrain. This dispersion is limited to a hemisphere by a wall located near the source and parallel to the wind (Fig. 2). The wall is located at a distance of 1 Lei (for instantaneous release) or 5.6 Lee (for continuous release) from the gas source. The wall is to be regarded as infinitely long and, during the heavy gas spread phase, as infinitely high (1Lei or 5.6 Lee).
Area map for dispersion area type III
Flat terrain. This dispersion takes place in a canyon of orthogonal walls. This canyon has a height of 1 Lei (for instantaneous release) or 7 Lee (for continuous release), and a breadth of 2 Lei or 28 Lee, respectively.
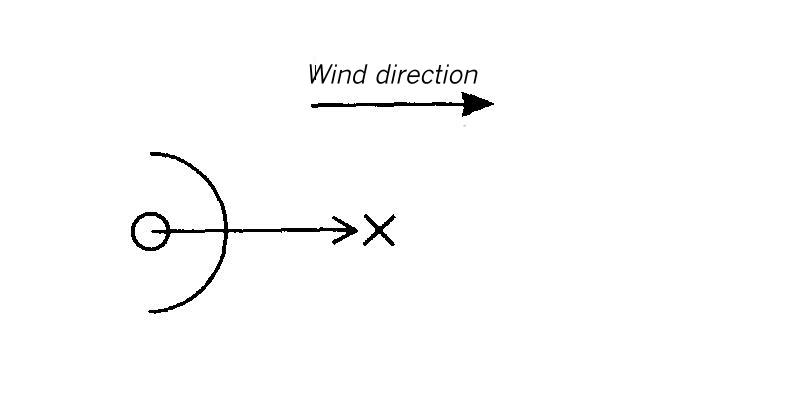
Area map for dispersion area type IV
Flat terrain. Semi-circular, massive wall leeward of the source. The height of the wall is 0.4 Lei (for instantaneous release) or 2.24 Lee (for continuous release). The distance between the source and the obstacle amounts to 4 Lei or 22.4 Lee, respectively.
Area map for dispersion area type V
Flat terrain. Semi-circular, massive wall leeward of the source. The height of the wall is 0.4 Lei (for instantaneous release) or 2.24 Lee (for continuous release). The distance between the source and the obstacle amounts to 2.5 Lei or 14 Lee, respectively.
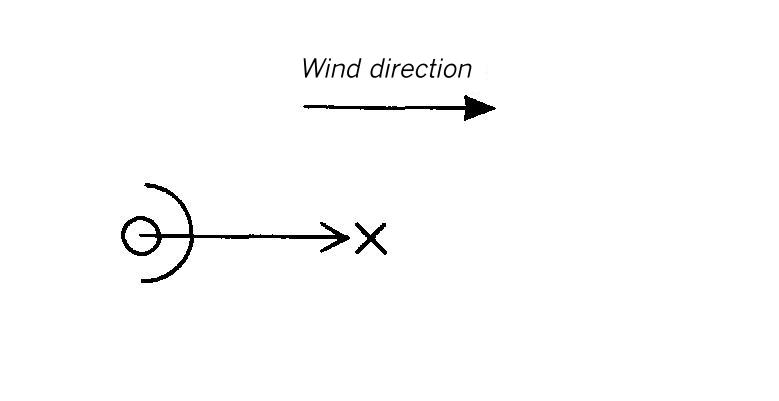
Dispersion area types VI to IX
Dispersion area type VI
In this dispersion area the wall, already used in dispersion area V, was placed in winward of the source. In contrast with the wall leeward of the source, in the dispersion area V no distinct protection is visible. The concentrations, however, are below those concentrations measured in the area without obstacles. As a reason for this, the shade of the area near the source is to be mentioned. This causes a stronger lateral dispersion of the gas cloud.
Dispersion area type VII
The wall used in this dispersion area corresponds to the obstacle used in the dispersion area IV. Just as in the dispersion area VI, the wall was placed here winward of the source. Although the concentrations are lower here than in the dispersion area without obstacles, not a significant protection is obtained by this obstacle.
Dispersion area type VIII
The obstacle in this dispersion area is in principle a combination of the obstacles used in the dispersion area types V and VI. The circular, impermeable protective wall with the source in the center used here, shows a great distinctive protection for all the locations situated downstream of the source leeward of the protection wall. The position of the protective wall is clearly the cause of the strong concentration gradient. As on the basis of the shade within the protective wall, the gas can spread stronger laterally than in the dispersion area type V, the concentration in the dispersion area VII is generally lower than in the dispersion area type V.
Dispersion area type IX
The circular, impermeable protective wall in this dispersion area corresponds to a combination of the obstacles in the dispersion area IV an VII. Also, as in the dispersion area type VIII, a great distinct protection for locations situated downstream of the source leeward of the protection wall is visible.
Area maps for types VI to IX
Area map for dispersion area type VI
Flat terrain. Semi-circular, massive wall windward of the source. The height of the wall is 0.4 Lei (for instantaneous release) or 2.24 Lee (for continuous release). The distance between the source and the obstacle amounts to 2.5 Lei or 14 Lcc, respectively.
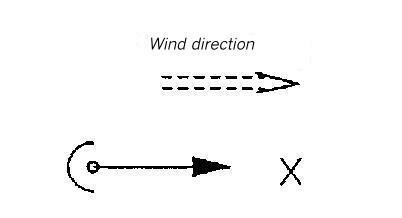
Area map for dispersion area type VII
Flat terrain. Hemispherical, massive wall in luv of the source. The height of the wall is 0.4 Lei (for instantaneous release) or 2.24 Lee (for continuous release). The distance between the obstacle and the source amounts to 4Lei or 22.4 Lcc, respectively.
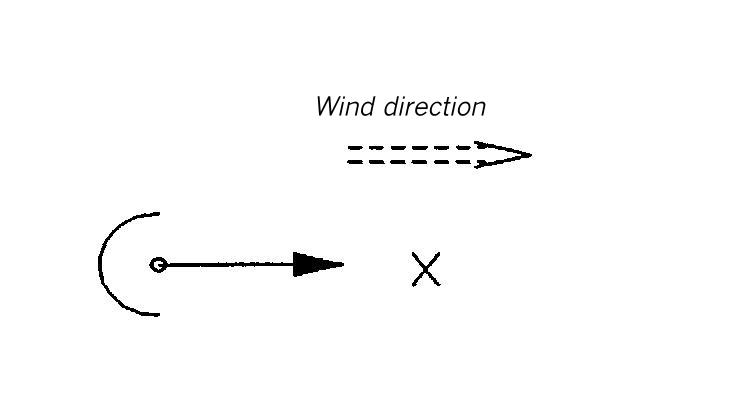
Area map for dispersion area type VIII
Flat terrain. Circular, massive wall around the source. The height of the wall is 0.4 Lei (for instantaneous release) or 2.24 Lee (for continuous release). The distance between the source and the obstacle (radius of the obstacle) amounts to 2.5 Lei or 14 Lcc, respectively.
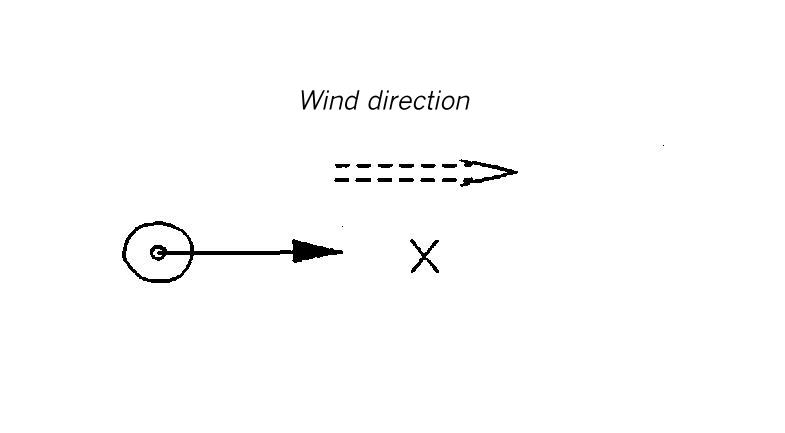
Area map for dispersion area type IX
Flat terrain. Circular, massive wall around the source. The height of the wall is 0,4 Lei (for instantaneous release) or 2,24 Lee (for continuous release). The distance between the source and the obstacle (radius of the obstacle) amounts to 4 Lei or 22,4 Lcc, respectively.
Dispersion area types X to XVIII
The dispersion area types X to XVIII can be used for accidental releases in which the dispersion is limited by an interrupted canyon of orthogonal walls which is parallel to the wind.
Dispersion area types X to XII
In case of an instantaneous release the measured mean UZD are generally lower in these dispersion areas than the UZD measured in an uninterrupted canyon (dispersion area type III). In the dispersion area type X (in continuous release) after 50 Lee distance from the source, lower UZD than in the dispersion area type III are visible, while the UZD in the dispersion area types XI and XII are generally lower than the values measured in the dispersion area type III.
The greater dilution of the heavy gas cloud is traced back to the greater mixing with ambient air. This is caused by the lateral building gaps.
As it is evident from the concentration courses, a widening of the canyon and the building gaps leads to a reduction of the UZD values.
Area maps for types X to XII
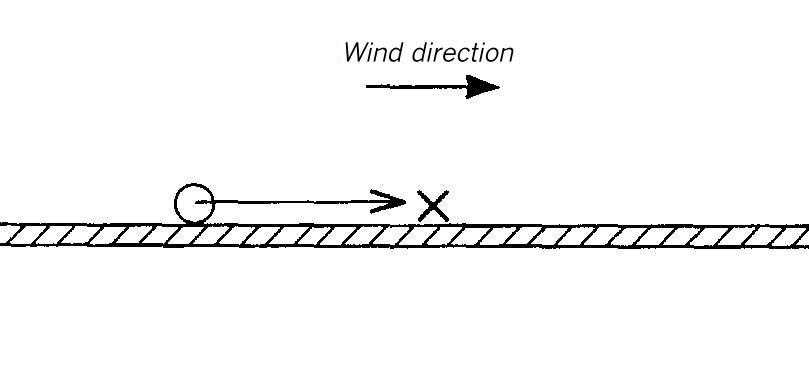
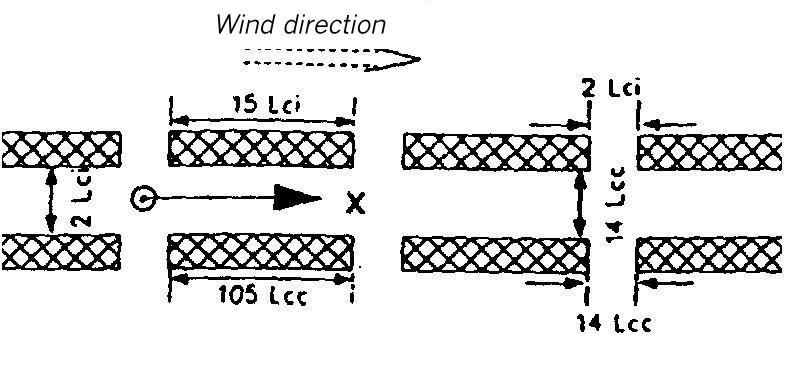
Area map for dispersion area type X
Flat terrain. The dispersion takes place within a canyon of orthogonal walls interrupted by lateral gaps. It is 1.5 Lei (for instantaneous release) or 11 Lee (for continuous release) high and 2 Lei or 14 Lee wide.
The lateral walls of the canyon consist of pieces which are 15 Lei or 105 Lee long and separated from each other by gaps which are 2 Lei or 14 Lee wide.
The source is located in the center of the canyon and in the center of a building gap.
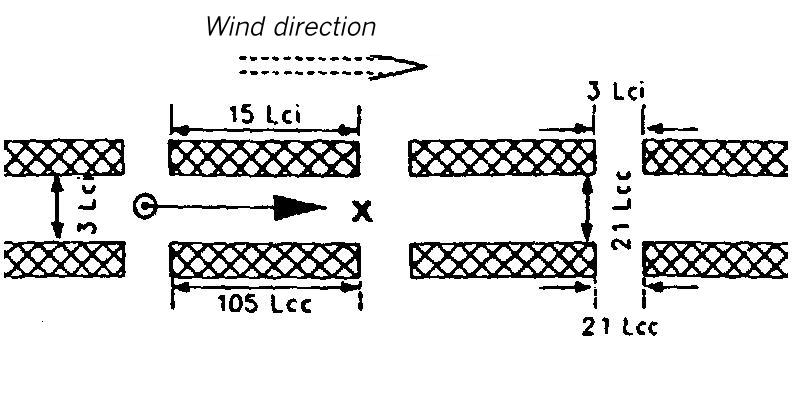
Area map for dispersion area type XI
Flat terrain. The dispersion takes place within a canyon of orthogonal walls interrupted by lateral gaps. It is 1.5 Lei (for instantaneous release) or 11 Lee (for continuous release) high and 3 Lei or 21 Lee wide.
The lateral walls of the canyon consist of pieces which are 15 Lei or 105 Lee long and separated from each other by gaps which are 3 Lei or 21 Lee wide.
The source is located in the center of the canyon and in the center of a building gap.
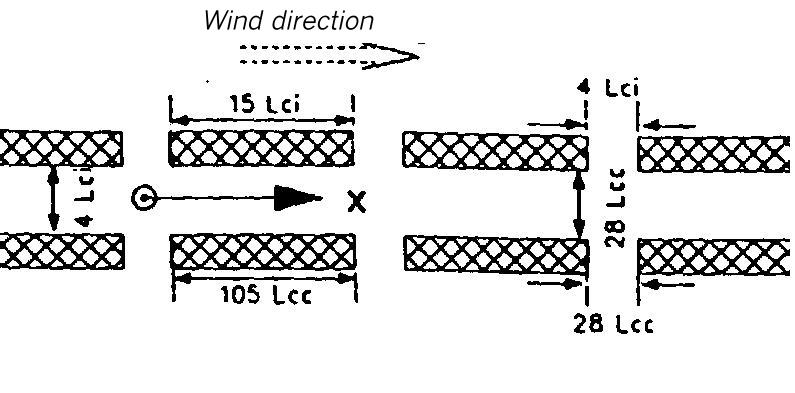
Area map for dispersion area type XII
Flat terrain. The dispersion takes place within a canyon of orthogonal walls interrupted by lateral gaps. It is 1.5 Lei (for instantaneous release) or 11 Lee (for continuous release) high and 4 Lei or 28 Lee wide.
The lateral walls of the canyon constist of pieces which are 15 Lei or 105 Lee long and separated from each other by gaps which are 4 Lei or 28 Lee wide.
The source is located in the center of the canyon and in the center of a building gap.
Dispersion area types XIII to XV
This dispersion area types can be used in principle for the same canyons as the dispersion area types X, XI and XXII, though with a source of different location. As well as in the area types X to XII, a widening of the canyon and the building gaps lead to a reduction of the UZD values.
In case of an instantaneous release the mean UZD values of the area types XIII to XV are generally lower than the UZD measured in the dispersion area type III. In the dispersion area types XIII, XIV and XV (in instantaneous release) the mean concentration values after a source distance of a maximum of15 to 20 Lei are already lower than in an area without obstacles.
In case of a continuous release, the measured mean UZD values in the range of 50 to 200 Lee in the area types XIII to XV drop below the values measured in the area type III. However, during the entire heavy gas spread phase, those values are greater than the values measured in the area without obstacles.
Area maps for types XIII to XV
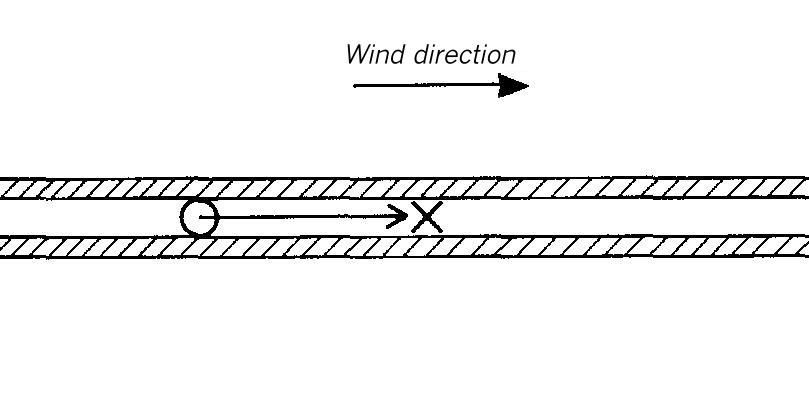
Area map for dispersion area type XIII
Flat terrain. The dispersion takes place in a canyon of orthogonal walls interrupted by lateral gaps. It is 1.5 Lei (for instantaneous release) or 11 Lee (for continuous release) high and 2 Lei or 14 Lee wide.
The lateral walls of the canyon consist of pieces which are 15 Lei or 105 Lee long and separated from each other by gaps which are 2 Lei or 14 Lee wide.
The source is located in the center of the canyon between two building gaps.
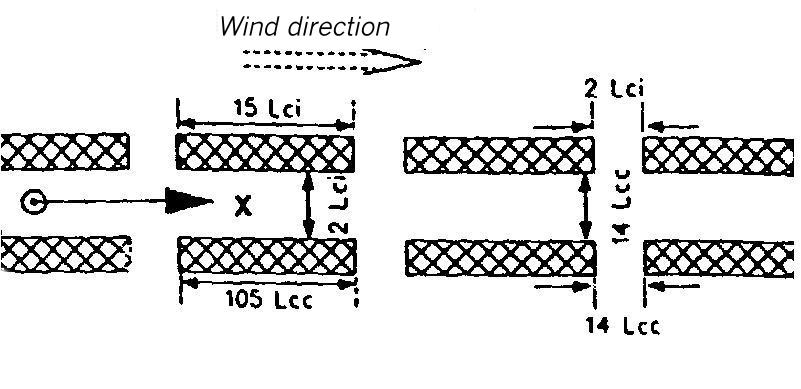
Area map for dispersion area type XIV
Flat terrain. The dispersion takes place within a canyon of orthogonal walls interrupted by lateral gaps. It is 1.5 Lei (for instantaneous release) or 11 Lee (for continuous release) high and 3 Lei or 21 Lee wide.
The lateral walls of the canyon consist of pieces which are 15 Lei or 105 Lee long and separated from each other by gaps which are 3 Lei or 21 Lee wide.
The source is located in the center of the canyon between two building gaps.
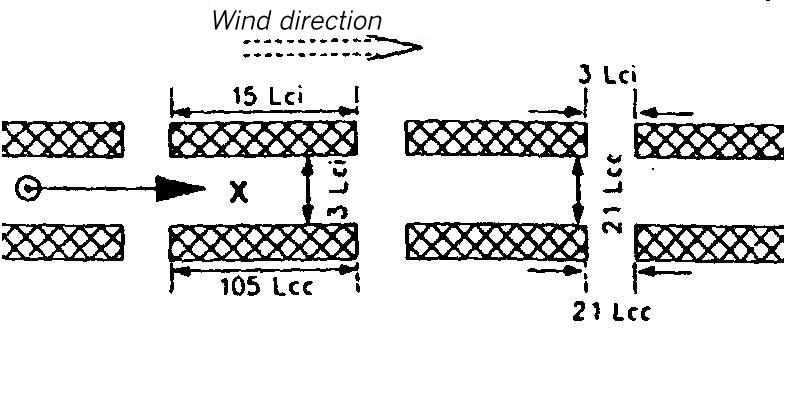
Area map for dispersion area type XV
Flat terrain. The dispersion takes place within a canyon of orthogonal wall interrupted by lateral gaps . It is 1.5 Lei (for instantaneous release) or 11 Lee (for continuous release) high and 4 Lei or 28 Lee wide.
The lateral walls of the canyon consist of pieces which are 15 Lei or 105 Lee long and separated from each other by gaps which are 4 Lei or 28 Lee wide.
The source is located in the center of the canyon between two building gaps.
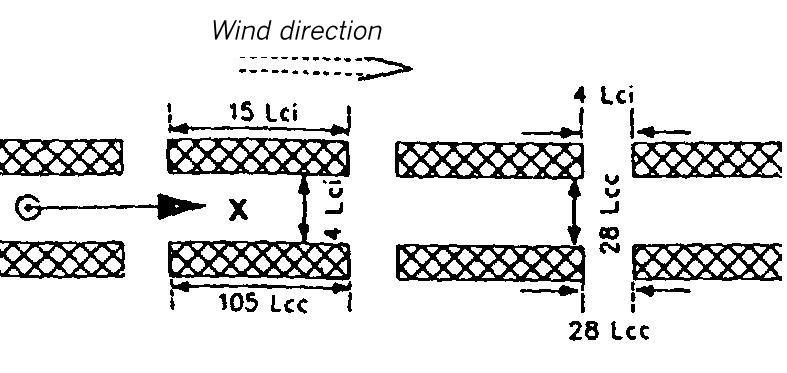
Dispersion area types XVI to XVIII
These dispersion areas can be used in principle for the same canyons as the dispersion area types X, XI and XII. However, the location of the source is moved upstream to the beginning of the building gap. A widening of the canyon and the building gaps leads to a reduction of the UZD values.
In instantaneous releases as well as in continuous releases, the mean UZD values measured in these areas are generally lower than the values measured in the dispersion area type III. In the dispersion area types XVI and XIII in instantaneous release, the mean UZD values are generally lower when there are no obstacles. This is also valid in case of continuous release for the dispersion area type XIII.
The mean UZD values are generally greater in the dispersion area type XI than in the dispersion area without obstacles. In the dispersion area type XVII the mean UZD values are at first lower than in the case without obstacles. Because of the reduced lateral dispersion of the cloud, the dilution proceeds slower than in the case without obstacles; and so the mean UZD values in the dispersion area type XVII from about 150 Lee distance from the source, are greater than the values measured in the area type I.
Area maps for types XVI to XVIII
Area map for dispersion area type XVI
Flat terrain. The dispersion takes place within a canyon of orthogonal walls interrupted by lateral gaps. It is 1.5 Lei (for instantaneous release) or 11 Lee (for continuous release) high and 2 Lei or 14 Lee wide.
The lateral walls of the canyon consist of pieces which are 15 Lei or 105 Lee long and separated from each other by gaps which are 2 Lei or 14 Lee wide.
The source is located in the center of the canyon at the beginning of a building gap.
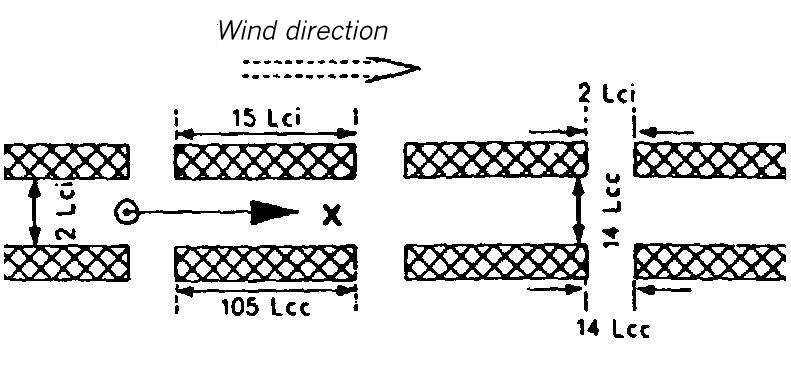
Area map for dispersion area type XVII
Flat terrain. The dispersion takes place within a canyon of orthogonal walls interrupted by lateral gaps. It is 1.5 Lei (for instantaneous release) or 11 Lee (for continuous release) high and 3 Lei or 21 Lee wide.
The lateral walls of the canyon consist of pieces which are 15 Lei or 105 Lee long and separated from each other by gaps which are 3 Lei or 21 Lee wide.
The source is located in the center of the canyon at the beginning of a building gap.
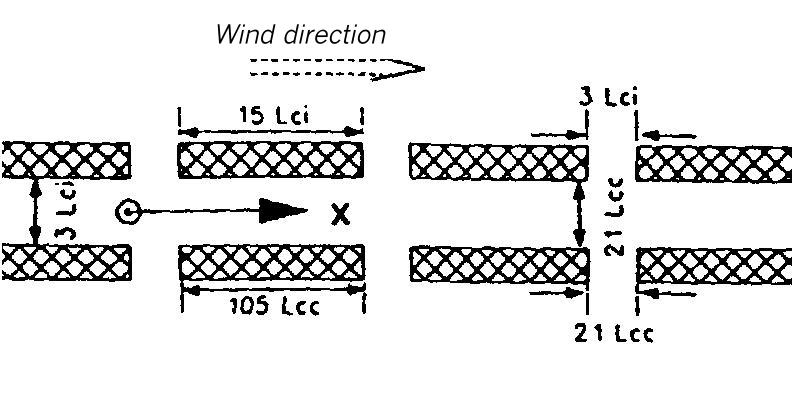
Area map for dispersion area type XVIII
Flat terrain. The dispersion takes place within a canyon of orthogonal walls interrupted by lateral gaps. It is 1,5 Lei (for instantaneous release) or 11 Lee (for continuous release) high and 4 Lei or 21 Lee wide.
The lateral walls of the canyon consist of pieces which are 15 Lei or 105 Lee long and separated from each other by gaps which are 4 Lei or 28 Lee wide.
The source is located in the center of the canyon at the beginning of a building gap.
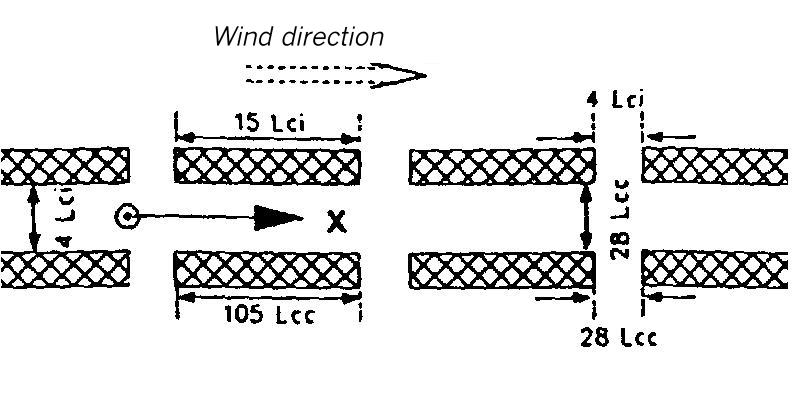
Dispersion area types XIX to XXI
The dispersion area types XIX to XXI can be used for accidental releases, in which the dispersion takes place within an area of interrupted uniform buildings.
In instantaneous as well as in continuous release, the mean UZD values measured in these dispersion area types are lower than the values measured in the area without obstacles (area type I). The greater dilution is traced back to the greater mixing with ambient air caused by the buildings.
As it is evident from the concentration courses, a further interruption of the buildings leads to rising UZD values until finally the UZD values of obstacle free cases are reached.
Area maps for types XIX to XXII
Area map for dispersion area type XIX
Flat terrain. The dispersion takes place within an area of uniform buildings. The height of the buildings is 1 Lei (for instantaneous release) or 11 Lee (for continuous release). The lateral measurements of the buildings elements amount to 1 Lei or 11 Lee. The distance from each other is 2 Lei or 21 Lee, respectively.
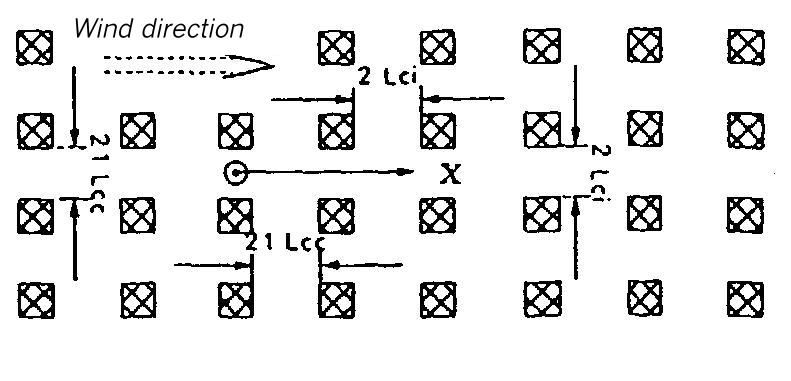
Area map for dispersion area type XX
Flat terrain. The dispersion takes place within an area of uniform buildings. The height of the buildings is 1 Lei (for instantaneous release) or 11 Lee (for continuous release). The lateral measurements of the buildings elements amount to 1 Lei or 11 Lee. The distance from each other is 2,5 Lei or 27 Lee, respectively.
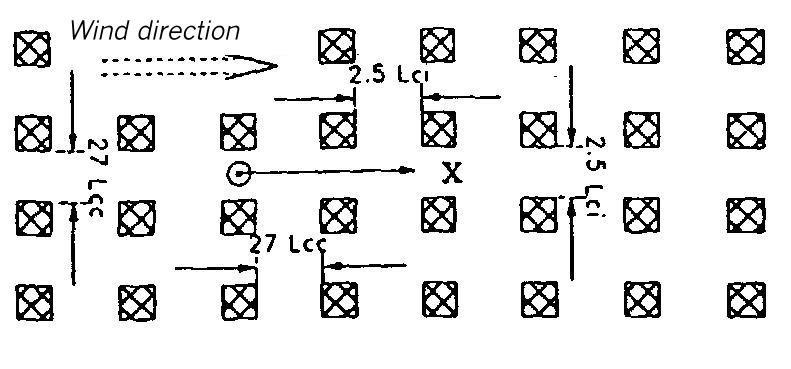
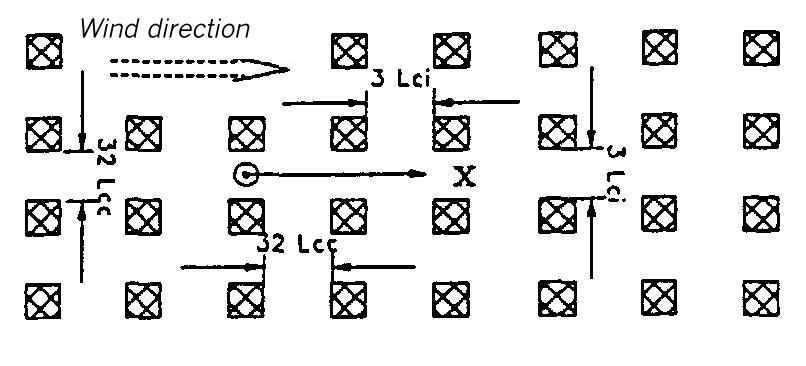
Area map for dispersion areas type XXI and XXII
Flat terrain. The dispersion takes place within an area of uniform buildings. The height of the buildings is 1 Lei (for instantaneous release) or 11 Lee (for continuous release). The lateral measurements of the buildings elements amount to 1 Lei or 11 Lee. The distance from each other is 3 Lei or 32 Lee, respectively.
XXI
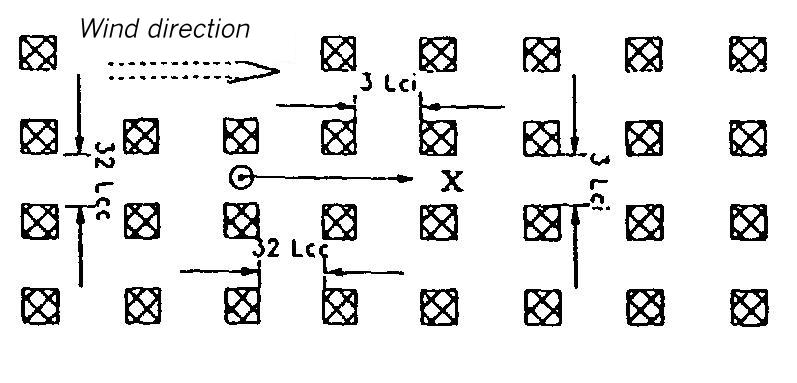
XXII
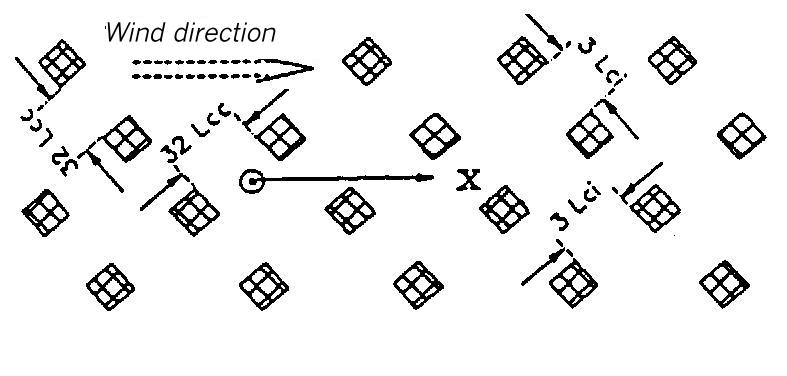
Area maps for types XXIII to XV
Area map for dispersion area type XXIII
Flat terrain. The dispersion takes place within an area of uniform buildings. The height of the buildings is 1 Lei (for instantaneous release) or 11 Lee (for continuous release). The lateral measurements of the buildings elements amount to 1 Lei or 11 Lee. The distance from each other is 5 Lei or 53 Lee, respectively.
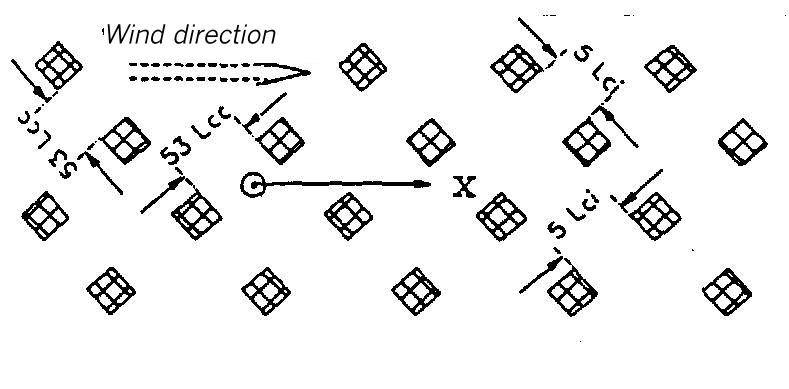
Area map for dispersion area type XXIV
Flat terrain. The dispersion takes place within an area of uniform buildings. The height of the buildings is 2 Lei (for instantaneous release) or 21 Lee (for continuous release). The lateral measurements of the buildings elements amount to 1 Lei or 11 Lee. The distance from each other is 3 Lei or 32 Lee, respectively.
Area map for dispersion area type XXV
Flat terrain. The dispersion takes places within an area of uniform buildings. The height of the buildings is 2 Lei (for instantaneous release) or 21 Lee (for continuous release). The lateral measurements of the building elements amount to 1 Lei or 11 Lee. The distance from each other is 4 Lei or 43 Lee, respectively.
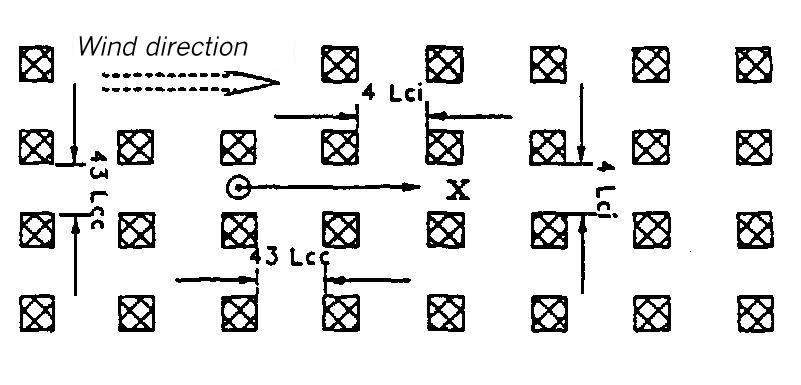
Definition of the input data for instantaneous release for the numerical model in Guideline VDI 3783 Part 1
| Dispersion area type | Delta Xmean [m] | Delta Xworst [m] | Delta tmean [s] | Delta tworst [s] |
| I | 36 Lei | 55 Lei | 65 Tei | 90 Tei |
| II | 50 Lei | 60 Lei | 95 Tei | 105 Tei |
| III | 65 Lei | 75 Lei | 160 Tei | 175 Tei |
| IV | 14 Lei | 19 Lei | 53 Tei | 59 Tei |
| V | 15 Lei | 20 Lei | 50 Tei | 55 Tei |
| VI | 28 Lei | 40 Lei | 60 Tei | 100 Tei |
| VII | 30 Lei | 48 Lei | 75 Tei | 120 Tei |
| VIII | 13 Lei | 16 Lei | 40 Tei | 44 Tei |
| IX | 15 Lei | 20 Lei | 33 Tei | 40 Tei |
| X | 30 Lei | 37 Lei | 80 Tei | 100 Tei |
| XI | 28 Lei | 35 Lei | 70 Tei | 90 Tei |
| XII | 27 Lei | 37 Lei | 50 Tei | 70 Tei |
| XIII | 31 Lei | 37 Lei | 85 Tei | 100 Tei |
| XIV | 30 Lei | 36 Lei | 80 Tei | 95 Tei |
| XV | 27 Lei | 33 Lei | 75 Tei | 90 Tei |
| XVI | 23 Lei | 30 Lei | 60 Tei | 80 Tei |
| XVII | 23 Lei | 31 Lei | 70 Tei | 95 Tei |
| XVIII | 25 Lei | 31 Lei | 65 Tei | 80 Tei |
| XIX | 19 Lei | 24 Lei | 40 Tei | 50 Tei |
| XX | 20 Lei | 24 Lei | 40 Tei | 50 Tei |
| XXI | 22 Lei | 28 Lei | 40 Tei | 50 Tei |
| XXII | 12 Lei | 18 Lei | 25 Tei | 35 Tei |
| XIII | 23 Lei | 29 Lei | 40 Tei | 50 Tei |
| XIV | 19 Lei | 26 Lei | 40 Tei | 45 Tei |
| XV | 20 Lei | 29 Lei | 45 Tei | 50 Tei |
Definition of the input data for continuous release for the numerical model in Guideline VDI 3783 Part 1
| Dispersion area type | Delta Xmean [m] | Delta Xworst [m] |
| I | 240 Lee | 296 Lee |
| II | 280 Lee | 400 Lee |
| III | 650 Lee | 700 Lee |
| IV | 90 Lee | 122 Lee |
| V | 112 Lee | 130 Lee |
| XI | 149 Lee | 182 Lee |
| XII | 134 Lee | 174 Lee |
| XIII | 102 Lee | 126 Lee |
| IX | 80 Lee | 108 Lee |
| X | 320 Lee | 435 Lee |
| XI | 265 Lee | 300 Lee |
| XII | 245 Lee | 325 Lee |
| XIII | 365 Lee | 490 Lee |
| XIV | 340 Lee | 390 Lee |
| XV | 270 Lee | 370 Lee |
| XVI | 275 Lee | 320 Lee |
| XVII | 245 Lee | 300 Lee |
| XVIII | 215 Lee | 250 Lee |
| XIX | 75 Lee | 118 Lee |
| XX | 105 Lee | 180 Lee |
| XXI | 128 Lee | 185 Lee |
| XXII | 57 Lee | 75 Lee |
| XXIII | 95 Lee | 150 Lee |
| XIV | 90 Lee | 130 Lee |
| XV | 128 Lee | 160 Lee |
* UZD (untere Zünddistanz) = lower flammability distance

